Solenoid valves are electronically operated devices that are used to control and direct the flow of gases or liquids. They are useful in situations that demand remote control of fluids or other media. There are several types of solenoid valves, and two way solenoid valves are the most common.
Basic Operation of Two Way Valves
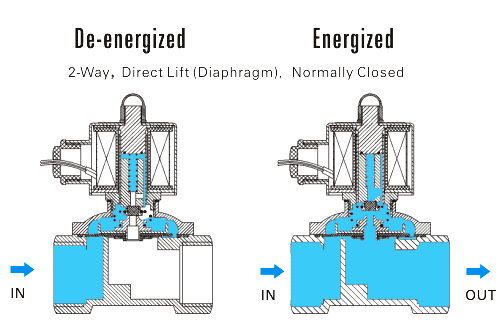
Just like the name suggests, a two way solenoid valve has one outlet and one inlet. This type of valve has basically two types of operation. In the Normally Closed (NC) operation, the coil is de-energized to shut off the fluid and it is energized to let the fluid flow through. Then there is the Normally Open (NO) operation in which the fluid flows when the coil is de-energized and is cut off when the coil is energized. The operation type should be noted in the solenoid valves symbols.
Basic Types of Two Way Valves
There are two basic methods of constructing two way solenoid valves for it to function.
There is Direct Lift and internally piloted construction. In direct acting construction, the diaphragm opens the NC valve or closes the NO valve when the coil is energized. The operating pressures for this construction range from zero psi to the valve’s maximum (and it depends on the particular manufacturer). These types of valves do not rely on the pressure of the media to open and close the diaphragm.
For the Internally Piloted valve type, a line pressure is used to assist in the operation of the valve. In this case, de-energizing the coil in the NC valve closes the pilot orifice, and line pressure is applied to the diaphragm thereby closing the valve. Energizing the coil, on the other hand, has the effect of opening the pilot orifice, which reduces the pressure on the diaphragm. This construction means that it is the line pressure that is solely responsible for opening the valve as it acts on the diaphragm. This construction is useful in operating large orifices with relatively small coils.